Continuous Control Acne Cleanser Ph Level
Nakaraj Pluetrattanabha, Kanokvalai Kulthanan, Piyavadee Nuchkull, Supenya Varothai
Department of Dermatology, Faculty of Medicine, Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
Correspondence Address:
Kanokvalai Kulthanan
Department of Dermatology, Faculty of Medicine, Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, 2 Wanglang Road, Bangkoknoi, Bangkok 10700
Thailand
Sir,
The effectiveness of cleansers is influenced by many factors including the pH, nature, and the composition of cleansers, especially surfactants. Our purpose was to study the pH of commonly available cleansers in the market for acne patients. The pH values of cleansing bars, liquid cleansers, foams, and scrubs promoted for acne patients were measured and compared with cleansers that are marketed for use on oily skin, baby skin, or sensitive skin (mild cleansers), as well as with general cleansers and antiseptic cleansers. All cleansers were dissolved to make a 5% solution (weight by volume) as per the actual usage condition. The pH was determined using a pH meter (Thermo Scien Oion 2 Star, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Beverly, MA, USA) and pH indicator strips (pH 0-14 Universal indicator strips; Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). Each sample was measured twice to obtain an average pH value.
The average pH values of cleansers are shown in [Table - 1], [Table - 2], [Table - 3]. All acne cleansing bars had an alkaline pH (pH 9.0-10.4), as was found in all other types of cleansing bars, except for syndet bar, which gave a neutral pH, and a cleansing bar for oily skin, which had an acidic pH [Table - 1]. The pH of liquid cleansers for acne (n = 9) ranged between 3.0 and 8.0 (5 = acidic pH, 3 = neutral pH, 1 = alkaline pH). Most of the other types of liquid cleansers had neutral pH, except for antiseptic cleansers [Table - 2].
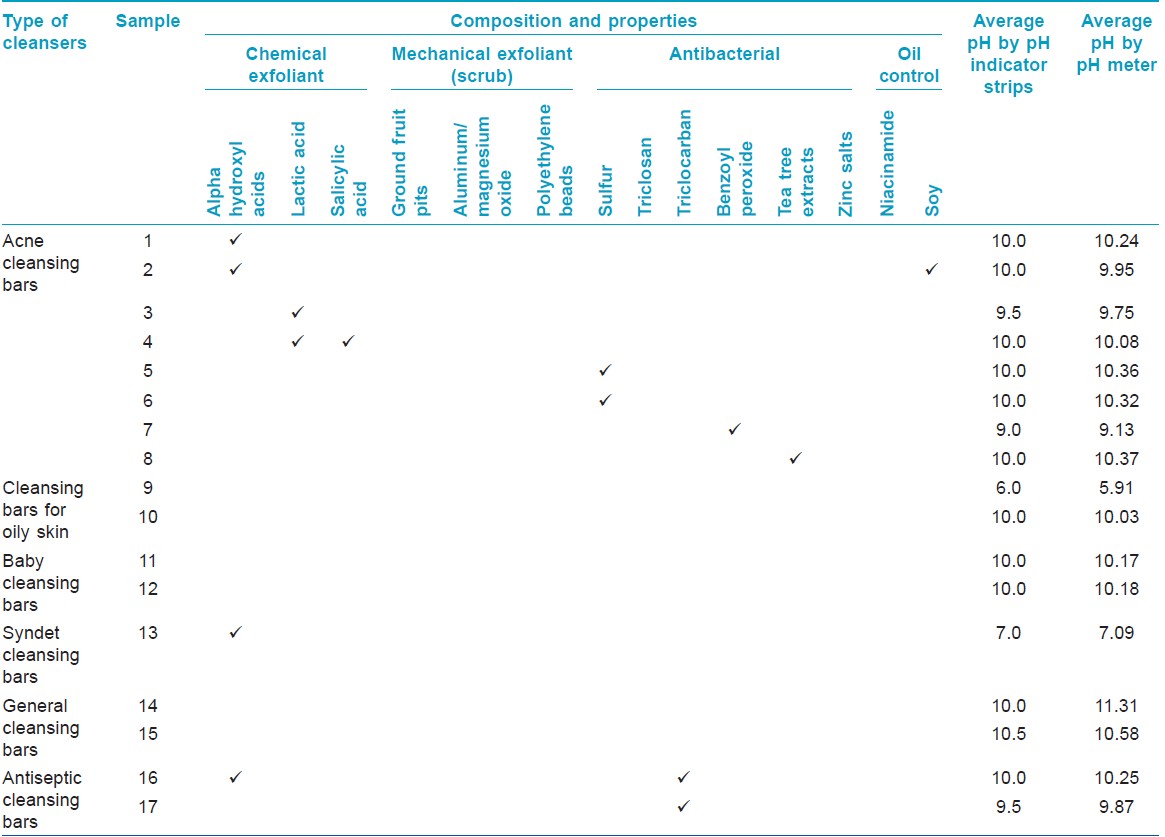
Table 1: Comparison of the pH values of acne cleansing bars and other cleansing bars
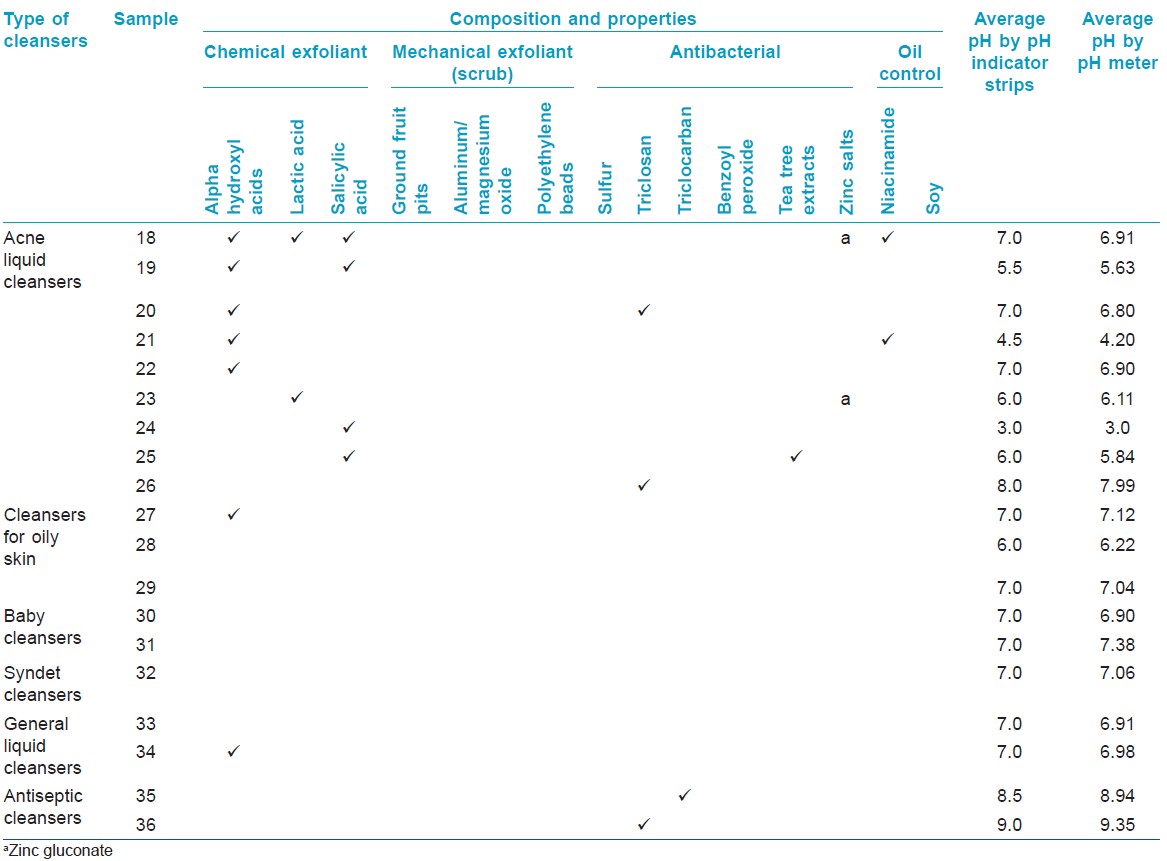
Table 2: Comparison of the pH of acne liquid cleansers and other liquid cleansers
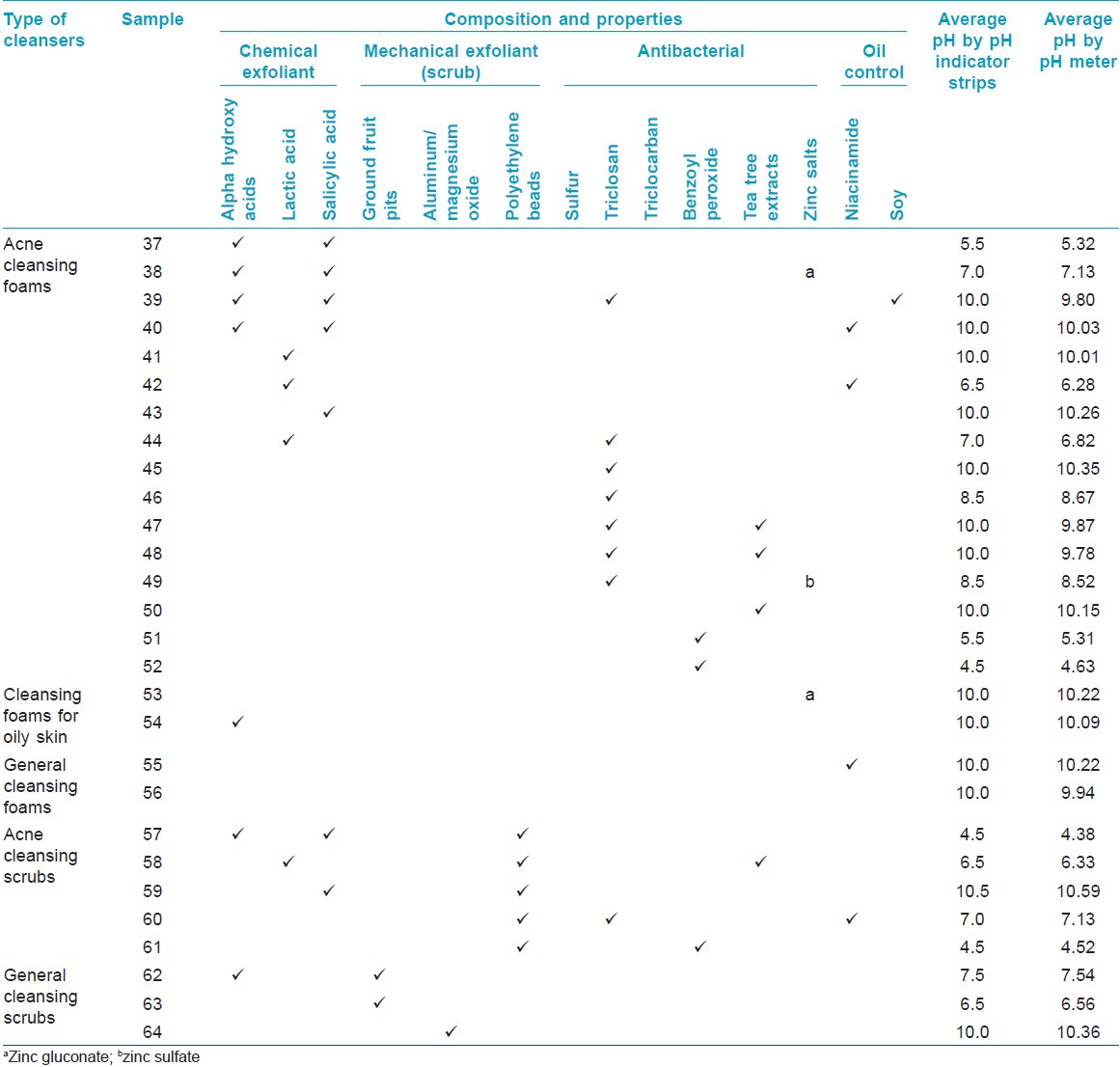
Table 3: Comparison of the pH of acne cleansing foams and scrubs and other cleansing foams and scrubs
[Table - 3] shows the pH of foams and scrubs. Most foams available in the market had an alkaline pH. The pH values of two acne foams were found to be similar to that of normal healthy skin (pH 5.4-5.9). Three acne scrubs were found to have an acidic pH and one each had a neutral and an alkaline pH [Table - 3].
Alteration of the skin pH is proposed to be one of the important factors for acne development, which may be due to the change of skin resident microflora. The skin pH can be influenced by many factors, i.e. genetics, age, gender, anatomical sites, skin moisture, sweat, sebum, soaps, detergents, cosmetics, and occlusive dressings. [1] Since the skin has an acidic pH, facial washing with soap can increase the pH level by 1.5-2.0. The increase in pH of cleansers potentiates skin dryness and tightness and also enhances the risk of cutaneous reactions. On the other hand, lowering the pH is supposed to benefit antibacterial effect. Goodman suggested that acne cleansers should be "soap-free," "acidic" or "pH-balanced," and free of abrasives or alcohols, and should also have high rinsibility. [2] It has been proposed that in order to control acne, the optimal value of skin pH should be 5.4-6.0 for females and 5.5 for males. [3]
In our study, it was found that all acne cleansing bars, in spite of various compositions, had an alkaline pH. Korting et al. compared the efficacy of an alkaline soap bar with an acidic syndet in 120 acne patients (a randomized controlled study) and found that after 3 months, the number of acne lesions and cutaneous irritation were lower in patients using an acidic syndet. [4]
In general, liquid cleansers have more acidic pH than those of cleansing bars since their compositions include amphoteric, anionic, non-ionic, and silicone surfactants. They also contain emollients and humectants which lower the pH of products. [5] In this study, liquid cleansers for acne were found to have a lower pH (pH 3.0-8.0) than those of acne cleansing bars (pH 9.0-10.0).
Foams are triphasic liquids composed of oil, organic solvents, and water. They are formulated with a hydrocarbon propellant (either butane or propane), and also contain various fatty acids and alkalis which influence their wide range of pH. [5] In this study, except for two brands, which had the pH of normal skin, all the others had an alkaline pH.
Facial scrubs are mechanical exfoliants. They contain small granules in a cleansing base for enhancing corneocyte desquamation. The proposed anti-acne property of scrubs is that the abrasion may unroof closed comedones. However, a vigorous scrub can damage the skin surface. Therefore, scrub should not be used more than once a week and is not recommended for patients with sensitive skin. Sixty percent of the tested scrubs for acne patients in this study showed an acidic pH.
In summary, the pH values of facial cleansers depend on their formulation and composition. The increase in pH potentiates skin dryness and tightness and also enhances the risk of cutaneous reactions. Apart from pH, other properties should be considered in selecting the proper cleansers for acne patients. [6]
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study would have not been possible without the support of Assistant Professor Leena Chularojanamontri. We would like to thank Dr. Kamolwan Pongparit for her support in manuscript preparation.
References
| 1. | Kim MK, Patel RA, Shinn AH, Choi SY, Byun HJ, Huh CH, et al. Evaluation of gender difference in skin type and pH. J Dermatol Sci 2006;41:153-6. [Google Scholar] |
| 2. | Goodman G. Cleansing and moisturizing in acne patients. Am J Clin Dermatol 2009;10:1-6. [Google Scholar] |
| 3. | Youn SH, Choi CW, Choi JW, Youn SW. The skin surface pH and its different influence on the development of acne lesion according to gender and age. Skin Res Technol 2013;19:131-6. [Google Scholar] |
| 4. | Korting HC, Ponce-Pöschl E, Klövekorn W, Schmötzer G, Arens-Corell M, Braun-Falco O. The influence of the regular use of a soap or an acidic syndet bar on pre-acne. Infection 1995;23:89-93. [Google Scholar] |
| 5. | Kuehl BL, Fyfe KS, Shear NH. Cutaneous cleansers. Skin Therapy Lett 2003;8:1-4. [Google Scholar] |
| 6. | Solomon BA, Shalita AR. Effects of detergents on acne. Clinics in Dermatol 1996;14:95-9. [Google Scholar] |
mcgreevymoafflurs.blogspot.com
Source: https://ijdvl.com/the-ph-of-skin-cleansers-for-acne/
0 Response to "Continuous Control Acne Cleanser Ph Level"
Post a Comment